2003 Polaris Freedom, Virage and Genesis PWC Service Manual, Page 129Get this manual
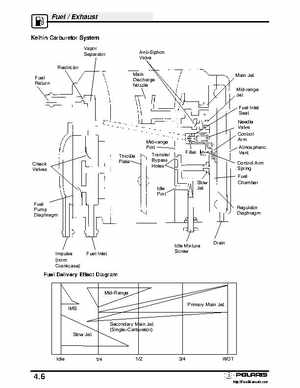
FuelExhaust Keihin Carburetor System OverviewContinued Pop Off Pressure
Carburetor pop-off pressure is pre-set at the factory for given engineTest as outlined on following pageIf pop-off pressure is incorrect, follow the procedure below to find the causePop-off pressure should not be changed to correct running condition problem unless required by changes in elevation, or enginecarburetor modifications for racingFuel inlet needle "pop off" pressure is influenced by many factorsAtmospheric pressure, venturi vacuum (low pressure), the amount of spring pressure on the control arm, fuel pressure from the fuel pump, and the size of the needle and seat all have an affect on operating pop off pressureAll of these forces combined regulate the amount of fuel that enters the carburetor fuel chamber and the engine
Needle ValveDiaphragm Operation
The amount of fuel allowed into the fuel chamber is controlled by the inlet needle valve assemblyOpening and closing of the valve is controlled by regulator diaphragm movement and spring pressure under the control armThe regulator diaphragm is sealed to the carburetor body forming two chambersOne side is vented to atmospheric pressure, the other side (fuel chamber) is connected to the venturi via the jets and passagesAtmospheric pressure pushes on one side of the diaphragm, applying pressure on the control arm in the fuel chamberThis reduces pressure on the inlet needle and allows it to lift more easily off the seatWhen the engine is running, pressure in the carburetor venturi (and therefore the fuel chamber) is less than atmosphericThis increases the effect of the atmospheric pressure on the diaphragm and leverWhen return spring pressure is overcome by these forces, the needle lifts off of the seat or "pops off", allowing pressurized fuel to enter the fuel chamberRegulator Diaphragm