Suzuki outboard motors 1988 2003 repair manual., Page 257Get this manual
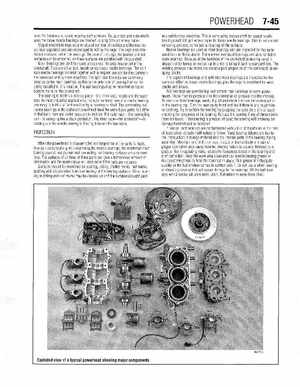
POWERHEAD 7-45 have the tendency to scoot, wearing both surfacesSo, journals and rods which uses the loose needle bearings are cleaned up sing 320 grit emery paperCaged needle bearings used reduced number of needles and the needles are kept separated and are encouraged to roll by the cageThe cage also controls end movement of the bearingsBecause of the cage, the journal and rod surfaces can be smoother, so these surfaces are polished with crocus clothMain bearings are used to mount and control the axial movement of the crankshaftThey are either ball, needle or split race needle bearingsThe split race needle bearings are held together with ring and are sandwiched between the crankcase and cylinder assemblyThe split race bearings are commonly used as center main bearings, as this is the only type of bearing that can be easily installed in this locationThe ball bearings may be mounted as top or bottom mains on the crankshaftThe bearing is made up of three parts-the inner race, needle and the outer raceIn most industrial applications, the outer or inner race of needle bearing assembly is held in fixed position by housing or shaftThe connecting rod needle bearings in the outboard powerhead have the same basic parts, but differ in that both inner and outer races are in motionThe outer race-the connecting rod-is swinging like clock pendulumThe inner race-the crankshaft-is rotating and the needle bearing is floating between the two racesto satisfactory conditionThis is done using crocus cloth for caged needle bearings and 320 grit emery paper for loose needle bearingsThis is not metal removing process, rather just clean up of the surfacesNeedle bearings are used as main bearings and are inspected for the same conditions as listed aboveThere are no oversized bearings available for rod or main bearingsBecause of the hardness of the crankshaft (a bearing race), it should not be turned or welded up in order to bring it back to standard sizeThe welding process may stress the metallurgical properties of the crankshaft, developing cracksThe caged rod bearings and split race main bearings are inspected for the same condition as loose needle bearings, plus the cage is examined for wear, cracks and breaksBall bearings are used for top and bottom main bearings in some powerheadsThese may be pressed onto the crankshaft or pressed into the end capTo examine these bearings, wash, dry, oil and check them on the crankshaft or in the bearing capTurn the bearing by hand and feel if there is any roughness or catchingTry to wobble the bearing by grasping the outer race, (inner race) checking for looseness of the bearingReplace the bearing if any of these conditions are foundIf the bearing is pressed off (out) the bearing will probably be damaged and should be replacedIf new or used bearings are contaminated with grit or dirt particles at the time of installation, abrasion will naturally followMany bearing failures are due to the introduction of foreign material into the internal parts of the bearing during assemblyMisalignment of the rod cap torque of the rod bolts and lack of proper lubrication also cause failuresBearing failure is usually detected by gradual rise in operating noise, excessive looseness (axial) in the bearing and shaft deflectionKeep the work area clean and use needle bearing grease or multipurpose grease to hold the bearings in placeThis grease will dissipate quickly as the fuel mixture comes in contact with itDo not use wheel bearing or chassis grease as this will cause damage to the bearingsOil the ball bearings with 2-stroke oil upon installationRemember to keep them cleanINSPECTION